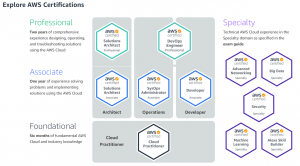
The Above picture explains career path and Certification of each role.
In this page, I will be explaining more about AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate. first few paragraphs are the same information from AWS documentation. but at the end of this blog, I have given more details of each domain and its contents. This is created for me to refer before going for the exam and to see that not missing anything. It helped me, so I think it will be helpful to other aspirants too.
Here is the recommended knowledge for SysOps admin exam
- Minimum of 1 year of hands-on experience with AWS
- Experience managing/operating systems on AWS
- Understanding of the AWS tenets – architecting for the cloud
- Hands-on experience with the AWS CLI and SDKs/API tools
- Understanding of network technologies as they relate to AWS
- Understanding of security concepts with hands-on experience in implementing security controls and compliance requirements
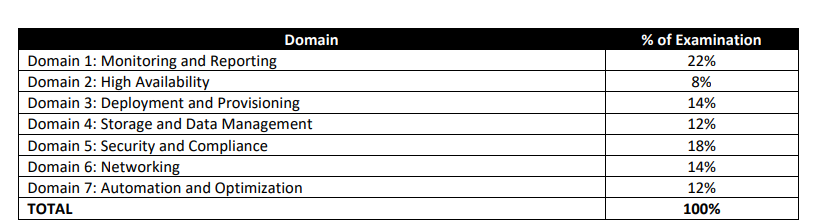
Domain 1: Monitoring and Reporting
1.1 Create and maintain metrics and alarms utilizing AWS monitoring services
1.2 Recognize and differentiate performance and availability metrics
1.3 Perform the steps necessary to remediate based on performance and availability metrics
Domain 2: High Availability
2.1 Implement scalability and elasticity based on use case
2.2 Recognize and differentiate highly available and resilient environments on AWS
Domain 3: Deployment and Provisioning
3.1 Identify and execute steps required to provision cloud resources
3.2 Identify and remediate deployment issues
Domain 4: Storage and Data Management
4.1 Create and manage data retention
4.2 Identify and implement data protection, encryption, and capacity planning needs
Domain 5: Security and Compliance
5.1 Implement and manage security policies on AWS
5.2 Implement access controls when using AWS
5.3 Differentiate between the roles and responsibility within the shared responsibility model
Domain 6: Networking
6.1 Apply AWS networking features
6.2 Implement connectivity services of AWS
6.3 Gather and interpret relevant information for network troubleshooting
Domain 7: Automation and Optimization
7.1 Use AWS services and features to manage and assess resource utilization
7.2 Employ cost-optimization strategies for efficient resource utilization
7.3 Automate manual or repeatable process to minimize management overhead
Click here to download Exam Guide for complete reference
Here are White papers for your reference (nice to read), Click to download
- Architecting for the Cloud: AWS Best Practices
- AWS Security Best Practices
- Amazon Web Services: Overview of Security Processes
- AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Development and Test on AWS
- Backup and Recovery Approaches Using AWS
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Connectivity Options
- How AWS Pricing Works
- Overview of deployment options on aws
Download Sample questions for practice
| Domain | % of exam | presentation time in minutes |
| Domain 1: Monitoring and Reporting | 22 | 45 |
| Domain 2: High Availability | 8 | 20 |
| Domain 3: Deployment and Provisioning | 14 | 30 |
| Domain 4: Storage and Data Management | 12 | 25 |
| Domain 5: Security and Compliance | 18 | 35 |
| Domain 6: Networking | 14 | 30 |
| Domain 7: Automation and Optimization | 12 | 25 |
| Total | 100 | 210 minutes |
Domain 1: Monitoring and Reporting
- AWS Cloudwatch
- cloud metrics of all AWS services(EC2, ASG, EBS, Elastic cache, redshift,RDS, Lambda) , alarms, aggregating metrics, custom metrics, high resolution-metrics, basic & detailed metrics
- cloudwatch log groups, Insights
- Events and rules
- AWS Cloudfront monitoring
- AWS Cloudtrails
- Cloudtrails, insights, logfile integrity
- AWS Config
- config aggregations of multiple accounts
- rules, resources
- Logs
- understand the difference between ELB logs and VPC logs. Also, go thru the use cases
- web ACL logs for WAF and its contents
- Route53 logs
- Also, understand how to stream application logs into cloudwatch
- filtering logs for specific words and alerting
- X-ray
- EC2config, EC2resque tool for windows servers
Domain 2: High Availability
- AWS Route 53
- Record types, mainly A-record, C-NAME. different use cases of CNAME and A records
- enabling logs, log format, fields of logs.
- health checks
- various routing policies (Simple routing policy, Failover routing policy, Geolocation routing policy, Geoproximity routing policy, Latency routing policy, Weighted routing policy and Multivalue answer routing policy)
- difference between latency routing and geolocation routing.
- Failover configuration for DR, weighted routing policy to divert traffic.
- AWS Cloudfront
- origin of Cloudfront
- difference between sessionid and signed URL
- Behaviours, Invalidations
- versioning and cache settings
- Geo restrictions
- Alarms, monitoring
- AWS ELB (Load balancer Application LB, Network LB and Classic LB)
- ELB cookies, application maintained cookies
- ELB health checks, integrating ELB hatchecks with ASG and Route53
- ELB pre-warmup requests
- ELB metrics especially Latency, SpilloverCount, SurgeQueueLength
- ASG
- groups and launch configurations
- setting alarms based on different use cases (EC2 metrics, SQS metrics)
- scaling policies (simple and step scaling)
- schedule scaling
- Life cycle hooks
- ASG monitoring ( metrics)
- VPC and on-premisis connections (Hybrid environments)
- VPC (default and custom)
- VPC peering
- VPC endpoints (gateway and interface)
- subnets, security groups, NACL, Elastic IP, NAT instance & NAT gateway
- site-to-site VPN, AWS Direct connect (choosing either of them as per use case)
- RDS replications in multi-AZ, availability in multiple regions
- Maintenance of multi-AZ, encriptions
- creating read replica in same or different availability zone. encryption scenario when replicas enabled in different region
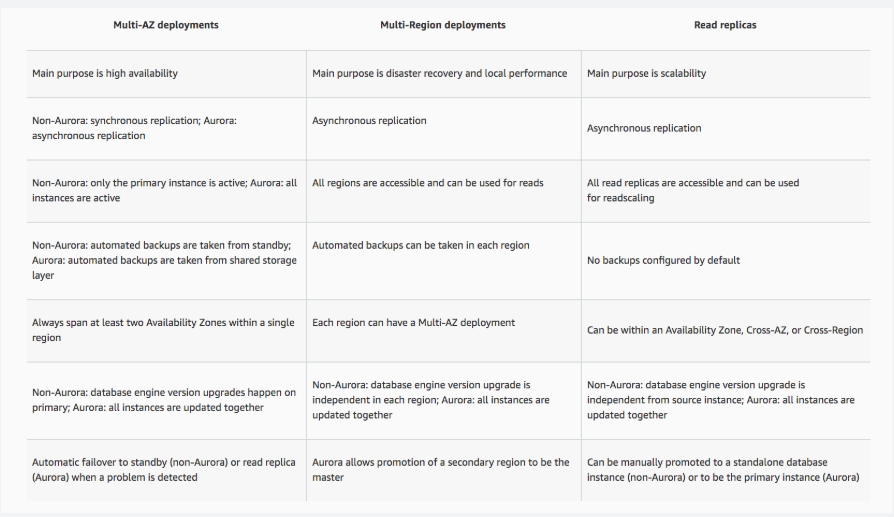
- when to use read replica and Elastic cache
- Elastic cache
- Improving the performance of Elastic cache (increasing the size and adding nodes)
- Elasticache evictions
- choosing between memcache and redis
- shards
Domain 3: Deployment and Provisioning
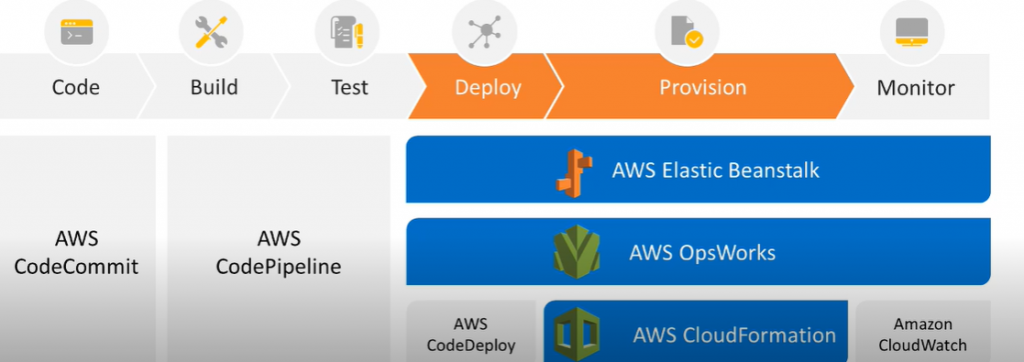
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Deployment policies
- advantages of Elastic Beanstalk over other deployment services like Cloudformation services
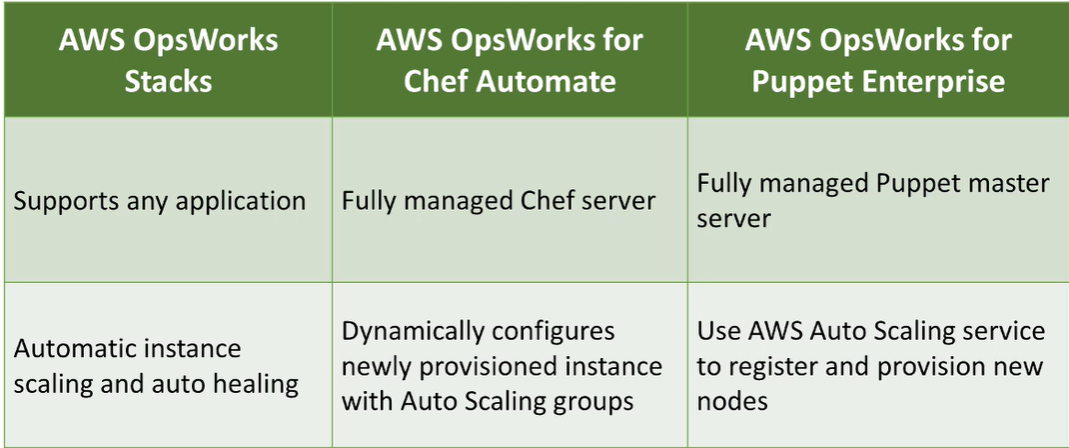
- AWS OpsWork
- stack, puppet and chef
- trouble shooting Opswork is commonly asked in sysops admin certification exam
- AWS Cloudformation
- cloudformation policies, helper scripts
- nested stacks, stacksets
- update stack sets, drifting
- AWS Service catalog
- Product and Portfolios (be sure to go thru the service catalog FAQs before going for the exam)
Domain 4: Storage and Data Management
- EBS Volumes
- snapshots, lifecyle, encryption, sharing snapshots across regions and AZ
- Instance stores
- Instance store life cycle, use cases
- EBS Snapshots
- EFS
- EFS performance modes, EFS monitoring metrics
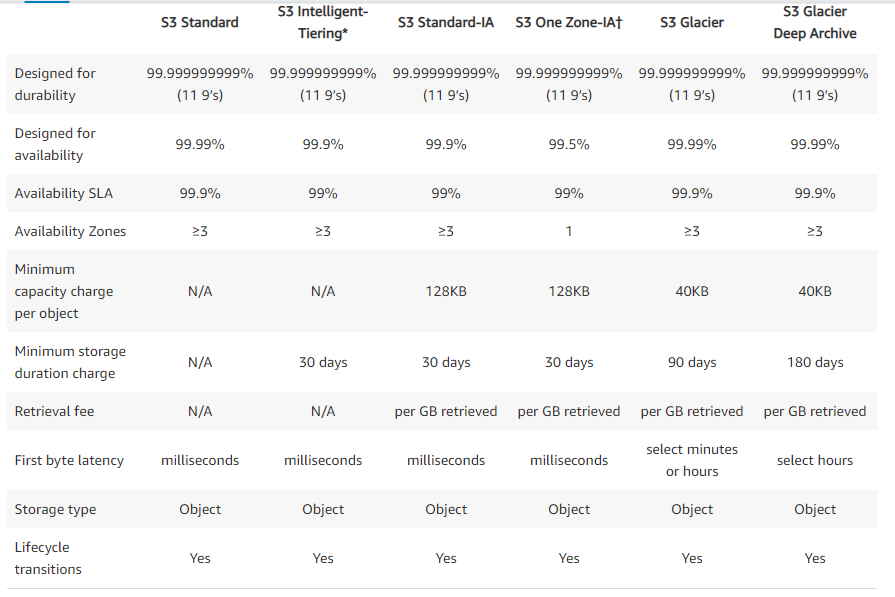
- S3
- S3 is one of the old services of AWS and expect lots of complex questions from this service
- S3 tiers
- S3 classes, ACL, policies (get smart on all soft of policies definitions )
- Encryptions
- static site hosting
- blocking access at bucket level and account level
- MFA delete, versioning
- life cycles
- Glacier
- Glacier tiers
- Vault lock policies, Vault access policies
- Archive retrial options
- Snowball and Snowball edge services
- understand when to use snowball and snowball edge services
Domain 5: Security and Compliance
- IAM
- There will lot of different questions comes from IAM for Sysops exam. so be well prepared with IAM. go thru FAQ and AWS documentation.
- roles, groups, policies
- STS, MFA, Cross account access
- Identity federation, SAML
- KMS
- CloudHSM
- AWS Inspector
- trouble shooting
- AWS GuardDuty
- Trusted Advisor
- features it support for different AWS support plans (e.g.: enabling alerts)
- AWS Cognito
Domain 6: Networking
- Route53
- public and private hosted zones, registering the domains, domains registered outside AWS
- VPC
- public and private subnets
- Security group and NACL
- NAT gateway, NAT instance
- Internet gateways
- IP4 and also IP6 support
- VPC end points
- VPC peering , Transtive peering
- DHCP option sets
- Cloudfront
Domain 7: Automation and Optimization
- Cloudformation
- optimizing the costs with reserve instances, spot instances
- optimizing the resource utilization with ASG, ELB